Inbound Marketing for SaaS: 8 Essential Strategies for Success
Discover 8 essential inbound marketing strategies for SaaS with our comprehensive guide.

Discover how the HubSpot Flywheel can transform your business by focusing on continuous customer engagement and satisfaction.
Older strategies for acquiring and retaining customers often do not cover many market story details. Introducing HubSpot flywheel, an inspiring system aimed at increasing inner growth, which implements customer-oriented strategies. In contrast to the previous models, where customers are regarded as assets that get bought, used, and discarded in a one-off fashion, the flywheel treats the whole process as a courtesy of attracting, satisfying, and maintaining loyalty in a circuitous way.
This blog examines the HubSpot flywheel and argues how its mechanics, benefits, and strategies can be harnessed to bring about long-term growth for organizations.
The HubSpot flywheel is a model that enhances the customer–business relationship through the core of every business system. It is a new approach, which takes away the sales funnel mindset, most often leading marketers to perceive a client relationship as only a one-shot transaction. But the focus of the flywheel is on repeating a series of interactions that result in excitement through retention and growth.
The flywheel is composed of three main stages:
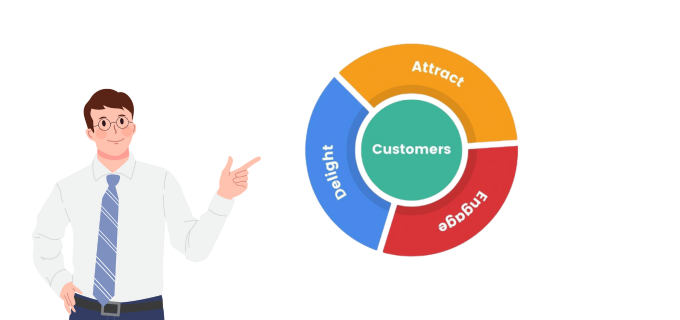
This stage consists of attracting potential customers to your business through content creation, search engine optimization, as well as other inbound marketing practices. The purpose is to grasp the target audience’s attention while creating recognition around the brand.
After attracting prospective clients, the next thing is to engage them with targeted marketing, relevant offers, and quality customer service. This level is mainly oriented towards relationship building and converting more prospects to faithful clients.
This is the last stage which aims at surpassing the clients’ expectations to gain their loyalty and strong support. Such experiences are responsible for positive referrals and reactions resulting in repeat sales that feed into the flywheel thus enhancing its gravity.
Numerous cases have been reported of the HubSpot flywheel being deployed across different industries, proving that this model is versatile for business expansion. This, however, does not sit well with this article. What are the strongest powers and weaknesses of the Flywheel Principles in various sectors?
Concerning the Software as a Service (SaaS) sector, the flywheel model is rather effective since it’s built on customer retention, which benefits the company in the long run. HubSpot for SaaS provides a wide range of capabilities to SaaS businesses to enhance their marketing efforts for more customer-centric growth. For example, a stereotypical SaaS company may begin by generating leads via insightful posts and educational webinars. These materials serve as answers to common business-related concerns and may gather potential customers who wish to enhance their businesses.
After this, the company takes them over with the help of product demos and such meetings where the customer is treated to a personal touch. The SaaS vendor does this by demonstrating their software capabilities regarding the particular need and problem at hand. Also, even though no more support is necessary, the target is responded to promptly and accurately every single time.
In the e-commerce business, the flywheel model emphasizes growth by providing impeccable customer experiences and ongoing interaction. For instance, an online seller may use various combinations of written SEO-optimized content, social media posts, and influencers to appeal to potential buyers. A fashion e-commerce business would e.g. feature on its website a blog on what is in fashion every season and use bloggers to present their new collections.
What drives customers is personalized engagement and personalized offers. For instance, the retailer may use filters and target customers through emails, providing different products within the customers' shopping history patterns. One or more supporting persons can also speak to the customers by employing a HubSpot live chat to assist with the shopper’s queries and their experience.
In particular, the flywheel model in financial services focuses on the notion of trust and value creation towards the customer. It is a common practice for a firm providing financial advisory services to offer potential clients free articles on investment strategies, guides for retirement planning, and webinars on various financial matters to try and generate a client base who might be interested in financial planning. All these aid in building the firm’s image and attracting potential clients with a rich interest in planning their financial future.
Customer engagement is driven by the direct one-on-one interaction they have with clients and the comprehensive financial plans they develop for such clients. A portfolio can be prescribed to a client based on recommendations made concerning the client’s circumstances within an agreed risk profile. Providing routine monitoring and also a periodic check of the finances eases and keeps the clients’ minds focused on their investment strategies.
Here are the advantages and disadvantages of HubSpot flywheel.
Narrowing to their Customers: The flywheel model improves on everything but turns to the customer focus leading to better relationships and loyalty. As such, they can implement competitive strategies of continuously reaching and satisfying the customers to lock them in and further grow their business when the customers promote it.
Long-term & Steady Growth: The flywheel is designed in a way that enables growth in the long term which is often not the case with most traditional models. This encourages relationship building that is aimed towards consistency in the business revenue and less resignation from customers.
Resonance with Inbound Marketing: Flywheel strategy being in a circle excludes any vacant spaces and each of its portions is distinct from other areas in terms that they all grow after inbound content creation, SEO practices, and active social media.
Gradient Problems: Moving from a funnel model to a flywheel is usually painful. It calls for change in processes, teams, and their ways of thinking to an extent that this may be met with some form of backlash or more training.
Difficult Metrics: Measuring the success of the flywheel tends to have more challenges than tracking the funnel model. Instead, new measurement methodologies about the customer are devised so that they can comprehend the in-depth nature and performance of their Flywheel strategy, including customer engagement, satisfaction, and the types of interactions they make.
The classical sales funnel model is typically predicated on seeking to steer prospects along a definitive trajectory from awareness through to a conversion objective. This practice usually culminates at the sale only without considering the retention or post-purchase activities.
On the other hand, the flywheel model seeks constant interaction with the customers. Unlike the traditional transaction that occurs only one-off, the flywheel leads to a constant cycle of customer attraction, engagement, and delight, which steers growth through customers’ advocacy. The key differences include:
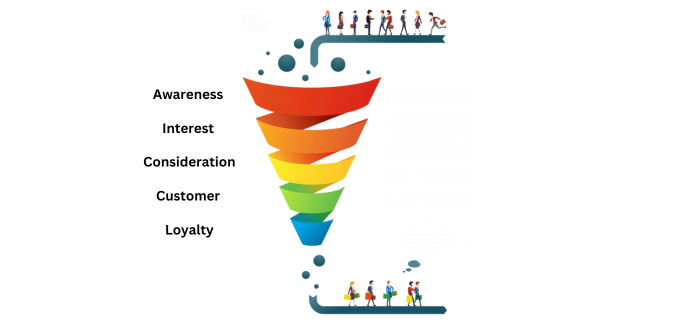
Funnel models, in particular, target new customers but the flywheel model aims at customer retention and development utilizing the existing customers.
Funnels illustrate a linear movement starting from awareness and ending with conversion while in the case of the flywheel, the customers go through successive stages that all work toward the customer branding the firm’s products.
The flywheel drives further growth through customer loyalty, whereas funnels come to an end with a focus on point of sale often neglecting any further customer interaction.
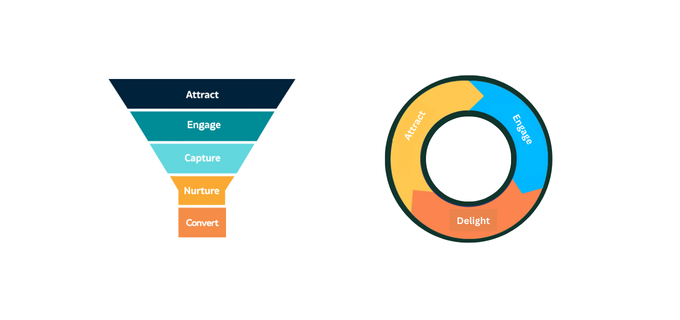
The three main elements of the inbound methodology, Attract, Engage, and Delight, are in great harmony with the flywheel model. The focus of both structures lies within the clients' experience value throughout the cycle.
Attract: The foremost stage, ‘Attract’, pulls potential customers into your brand and this is where inbound marketing practices like content creation, SEO, and social media come in handy.
Engage: The second stage: Engage correlates with the usage of inbound techniques including customized interaction, special deals, and nurturing of leads.
Delight: In the final stage, delight associates itself with satisfactory experiences concerning the healthy service offered to the clients, where the customer support team and other departments tend to the client’s needs to ensure that they remain loyal to the brand and actively advocate for it.
The flywheel can be fitted into the conduct of inbound marketing by creating blogs and other forms of content to attract and captivate the customers and, organizations who intend to incur the ‘wow’ factor in their customers can incorporate service elements to please the customer. For example, a company might use blog posts to draw in leads and emails to engage these leads who will further be offered superior customer services and great deals to enhance their current level of satisfaction.
Aligning the HubSpot flywheel with the existing organizational structures and practices necessitates a well-defined plan and cooperation among different departments:
The first step is determining some crucial touch points across the customer journey. Learn how customers approach your business at different stages. That is Attract, Engage, and Delight.
There should be synergy between marketing, sales, and client teams. Implementing a flywheel strategy requires input from all departments on how to maximize the client’s experience.
Apply all available HubSpot tools, such as CRM, marketing automation, and customer support software, in all stages of the flywheel. Such tools facilitate task execution, customer engagement, and personalization of communications.
The only way to keep the flywheel moving is by ensuring that the customers remain delighted. Employ ideas like special promotions, addiction to client well-wishes with messages, and client support to maintain healthy levels of the customer.
Do not sit back comfortably after erecting the flywheel. Frequently evaluate your flywheel’s performance and look toward the progress of this growth strategy. Use analytics and feedback to see which areas need more work and adapt them to be more effective.
The flywheel helps businesses deepen their relationship with customers, sustainably enhance their business, and equally adhere to inbound marketing principles by ensuring customers are at the core of the business strategy.
Accepting the flywheel may be difficult, yet the benefits that can be reaped in terms of repeat business and the chances of doing successful business over the long-term prospects are more attractive to the businesses. Using the flywheel, new avenues of growth are always available, helping fasten up progress in the business through the use of strategies that are focused on the clients.

Discover 8 essential inbound marketing strategies for SaaS with our comprehensive guide.

Explore strategic insights for business growth as we guide you through the 7 Stages of SaaS Customer Lifecycle.

Exploring strategies that power effective SaaS lead scoring. Boost business growth by understanding how to identify and prioritize high-value SaaS...